Understanding Basic Shapes
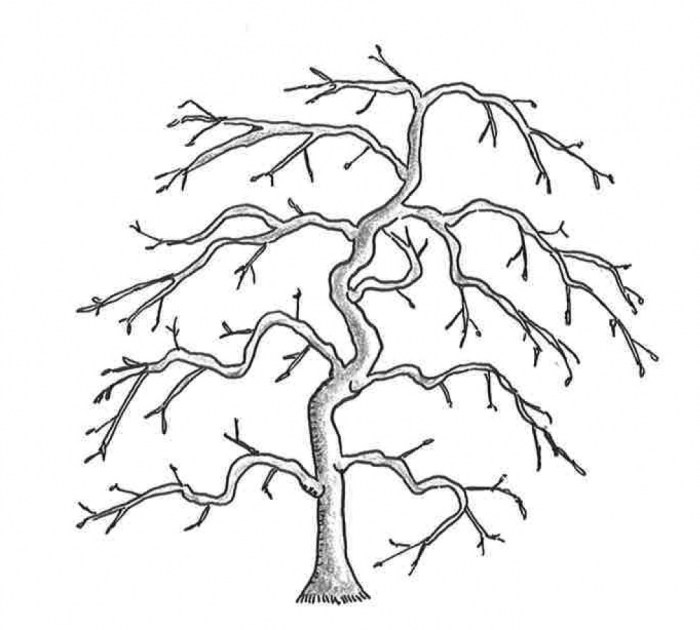
Japanese maple tree drawing easy – Drawing a Japanese Maple, with its intricate branching and delicate leaves, might seem daunting. However, breaking down the tree’s structure into basic geometric shapes simplifies the process considerably. By mastering this approach, you can accurately and efficiently capture the essence of this elegant tree.Simplifying the complex network of branches into manageable shapes is key to a successful drawing. This allows for a more controlled and intuitive approach, moving from a foundational structure to a detailed representation.
Geometric Foundations of Japanese Maple Structure
The overall silhouette of a Japanese Maple can often be approximated by an inverted triangle, with the widest part at the top and tapering down to a narrower base. Individual branches, however, are best understood through a combination of shapes. Thicker, main branches can be seen as elongated cylinders or slightly curved rectangles. As branches subdivide, they can be simplified into progressively smaller cylinders, or even as simple lines for the very thinnest twigs.
The leaves themselves, depending on the level of detail desired, can be represented as circles, ovals, or even simple rounded triangles.
Step-by-Step Branch Simplification
1. Identify the Main Trunk
Begin by identifying the main trunk of the tree. Visualize it as a slightly tapered cylinder or a rectangle with rounded edges. Sketch this foundational shape lightly.
2. Major Branch Division
Observe the major branches extending from the trunk. Note their angles and relative lengths. Simplify each into elongated cylinders or slightly curved rectangles, mirroring their actual shapes. Keep the sketches light at this stage.
3. Sub-branching
Divide the major branches into smaller ones. Again, use cylinders or rectangles, but gradually reducing their size and thickness as you move outward. For the finest branches, you might use simple lines.
4. Refinement
Once you have the basic branch structure laid out, you can begin to refine the shapes, adding subtle curves and variations in thickness to create a more natural look.
Japanese Maple Silhouettes Using Basic Shapes
A simple silhouette can be created using an inverted triangle for the overall form. Then, add a few slightly curved lines to represent the main branches extending from the trunk, creating a more realistic, albeit simplified, representation. A more detailed silhouette could involve several inverted triangles of varying sizes, nested within each other to suggest depth and layering of branches.
Another option is to use a combination of circles and ovals to represent the crown, with lines extending downwards to illustrate the main branches, resulting in a more abstract yet recognizable Japanese Maple silhouette. The choice depends on the desired level of detail and artistic style.
Leaf Structure and Detail: Japanese Maple Tree Drawing Easy
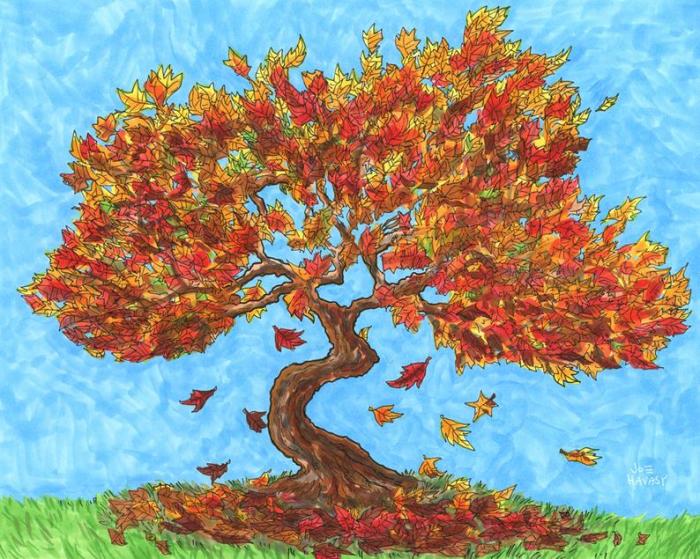

Japanese Maple leaves are iconic for their intricate beauty, a key element in accurately depicting these trees. Understanding their structure is crucial for creating convincing drawings, moving beyond simple shapes to capture their unique character. This section will detail the leaf’s shape, variations, and methods for rendering them with texture and veins.The characteristic shape of a Japanese Maple leaf is palmate, meaning it resembles a hand with outstretched fingers.
These “fingers” are called lobes, and their number varies considerably depending on the specific cultivar. While five lobes are common, some varieties exhibit three, seven, or even more. The lobes themselves are often pointed, with serrated edges adding further complexity. The overall leaf shape can range from deeply incised, creating a delicate, lacy appearance, to more rounded and less deeply cut forms.
Color variations also contribute to the leaf’s unique visual appeal, changing dramatically through the seasons.
Simplified Leaf Drawing Method
A straightforward approach to drawing individual leaves begins with a simple Artikel. Start by sketching a central axis, then draw the lobes radiating outwards. Focus on the number of lobes and their slightly uneven spacing to avoid a symmetrical, artificial look. Remember, the lobes are not perfectly uniform in size or shape; this natural asymmetry is key to realism.
Achieving a realistic depiction of a Japanese maple tree, with its intricate branching and delicate leaves, can be a rewarding artistic challenge. The level of detail required contrasts sharply with simpler subjects like a portrait, for instance, finding a tutorial for saddam hussein drawing easy would likely involve a far less complex approach. Returning to the Japanese maple, focusing on basic shapes before adding finer details is key to success.
For example, a five-lobed leaf might have one central lobe slightly larger than the others, with the lateral lobes progressively smaller towards the edges. This approach allows for easy replication of leaves with differing lobe counts, simply by adjusting the number of radiating lines from the central axis. Subtle variations in the lobe’s pointed tips and the depth of the sinuses (the spaces between the lobes) further enhance realism.
Adding Texture and Veins, Japanese maple tree drawing easy
Adding texture and veins enhances the realism of your drawing. For texture, avoid overly detailed shading. Instead, use subtle variations in tone to suggest the slightly crinkled surface of the leaf. Light strokes along the veins can create the impression of a three-dimensional surface, with the veins appearing slightly raised or recessed depending on the lighting. For veins, begin by lightly sketching the main central vein, then branch out with finer lines to depict the secondary and tertiary veins.
These finer veins should be less prominent and less defined than the main central vein. Don’t be afraid to leave some areas un-veined for a more natural, less uniform appearance. The veins should not be perfectly straight; gentle curves and variations in their thickness will add to the natural look. The veins will also often follow the shape of the lobe, creating a subtle curvature that reflects the leaf’s form.
Branching Patterns and Trunk
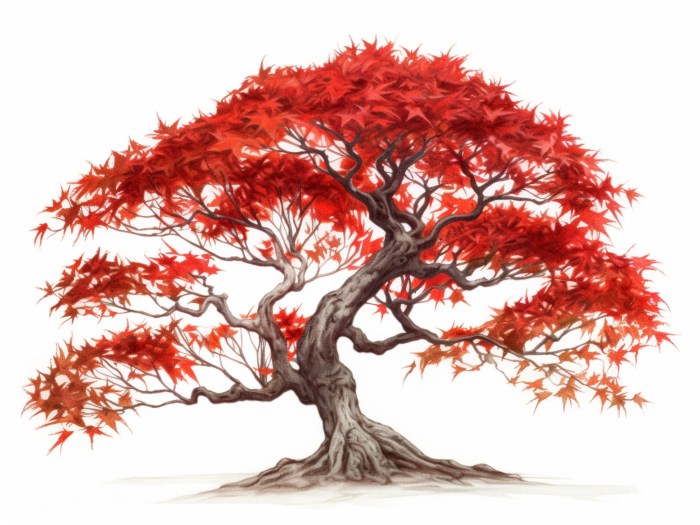

Creating a convincing Japanese Maple requires understanding its unique branching structure. The overall form, from the thick trunk to the delicate, outstretched branches, is crucial in capturing the essence of this elegant tree. The branching pattern directly influences the overall shape and aesthetic appeal of your drawing.The trunk forms the foundation of the entire tree. Its thickness, texture, and subtle curves dictate the character and age of the maple.
Consider the tree’s age when determining trunk thickness; a young sapling will have a slender trunk, while an older tree will boast a thicker, more robust one. The texture of the bark, often rough and furrowed in older trees, can be suggested through subtle shading and line variations.
Trunk Depiction
The trunk’s depiction begins with a central vertical line, representing the tree’s main axis. From this line, gradually build the trunk’s width, considering perspective and the tree’s overall posture. Avoid a perfectly straight line; incorporate gentle curves and subtle tapering to enhance realism. To suggest the texture of the bark, use short, slightly irregular lines to create the appearance of furrows and crevices.
In older trees, these textures are more pronounced, while younger trees have smoother bark. Shading can further emphasize the three-dimensionality and texture of the trunk. For instance, darker shading on the side facing away from a light source will create a sense of depth and volume.
Branching Structures
Japanese Maples exhibit diverse branching styles. Some varieties display an upright, vase-shaped form, with branches ascending gracefully from the trunk. Others feature a weeping or cascading habit, where branches droop elegantly downwards. Still others present a more rounded or spreading form. These variations stem from the tree’s genetics and environmental factors.Consider the upward reaching branches of an upright Japanese Maple.
These branches often emerge from the trunk at relatively wide angles, gradually becoming thinner and more numerous as they extend outwards. In contrast, the weeping variety displays a more pendulous branching structure, with branches curving downwards in a graceful cascade. The artist should carefully observe and depict these differences in branching angles and directions to accurately represent the chosen variety.
The overall density of branches also contributes to the tree’s appearance. A densely branched tree will appear fuller and more mature, while a sparsely branched tree will convey a sense of youth or perhaps a more delicate, refined aesthetic.
Branch Thickness and Distribution
Branch thickness is inversely proportional to distance from the trunk. The main branches are thicker, gradually diminishing in size as they subdivide into smaller twigs and branches. The distribution of branches is rarely uniform; they tend to cluster in some areas and spread more sparsely in others. This uneven distribution adds to the natural and organic look of the tree.
To achieve this, avoid a symmetrical or overly regular pattern. Instead, let the branches appear to grow organically, with some overlapping or intersecting each other. The spacing between branches should also vary, mimicking the natural irregularities found in real trees.
Illustrative Examples
This section provides three examples of Japanese Maple tree drawings, showcasing varying levels of detail to illustrate the progression from simple to complex representations. Each example demonstrates the application of the previously discussed principles of shape, leaf structure, branching, and trunk portrayal.
|
Example 1: Simplified Silhouette This drawing focuses on the overall form of the Japanese Maple. The trunk is represented as a single, slightly irregular line, branching into a few main limbs. The leaves are simplified into rounded masses, suggesting the overall shape of the foliage rather than individual leaves. The color palette is limited, perhaps to a single shade of green or red, depending on the season being depicted. The overall effect is a simple, easily recognizable representation of the tree. |
Example 2: Mid-Level Detail This example introduces more detail to the trunk and branches, showing some texture and variation in thickness. Individual leaves are now visible, though they are still simplified in shape, perhaps using a combination of ovals and rounded triangles. Variations in leaf color and shading can be added to suggest depth and light. The branching pattern is more complex, creating a more natural-looking canopy. This level of detail requires a slightly more skilled hand but remains accessible to intermediate learners. |
Example 3: Highly Detailed Representation This drawing aims for a realistic portrayal of a Japanese Maple. The trunk is detailed with texture, showing variations in bark and possibly even knots. Branches are intricately rendered, showing smaller twigs and variations in thickness. Individual leaves are carefully drawn, showing their palmate shape, serrated edges, and variations in size and orientation. The color palette is rich, with shading and highlights to create depth and realism. This level of detail requires significant skill and patience. |
FAQ Explained
What type of pencils are best for drawing Japanese Maple trees?
HB, 2B, and 4B pencils offer a good range for sketching, outlining, and shading. Experiment to find your preferred combination.
How do I achieve realistic leaf color variations?
Use layered colors. Start with a base layer, then add subtle variations of reds, oranges, and yellows for depth and realism. Experiment with blending techniques.
Can I use other mediums besides pencils?
Absolutely! Colored pencils, watercolors, and even inks can be used to create beautiful Japanese Maple tree drawings. The choice depends on your personal preference and desired style.
How important is perspective in drawing a Japanese Maple?
Perspective adds depth and realism. Consider the placement of the tree within the scene and how branches recede into the background. Simple perspective techniques can significantly enhance your drawing.


